The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation’s Citywide Inclusive Sanitation (CWIS) initiative includes direct support to eight cities across Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia that are redesigning their urban sanitation service systems with a CWIS approach. This approach is aimed at advancing safe, equitable, and sustained services across each city, with a focus on ensuring services reach women, girls, and low-income communities. The Foundation defines CWIS as follows:
Citywide Inclusive Sanitation (CWIS) is a public service approach to advance Equitable, Safe, and Sustainable outcomes, by strengthening the design and implementation of core public system functions of Responsibility, Accountability, and Resource Planning and Management.
Resources—human, financial, natural, assets—are effectively managed to support execution of mandate across time/space.
• Sanitation budget allocation is based on mandate and performance across service areas
• Sanitation investment decisions are driven by impact and cost considerations (including reliance on water and energy relative to their availability and cost) and are technology agnostic
• Sanitation planning is pro-poor, gender intentional, and inclusive
Authorities’ performance against their mandate is monitored and managed with data, transparency and incentives.
• Service authority performance is monitored with clear KPIs and targets
• Service authority performance is managed with data-driven incentives and/or penalties
• Accountability process is inclusive of customer and non-customer engagement, including marginalized voices
Authority(ies) executes a clear public mandate to ensure safe, equitable, and sustainable sanitation for all.
• Clear and non-overlapping mandate covering the entire service chain
• Mandates cover all urban areas without exclusions related to land tenure or artificial administrative boundaries
• Mandate is explicitly pro- poor, gender intentional, and inclusive of other vulnerable groups or status
Services reflect fairness in distribution and prioritization of service quality, prices, and deployment of public finance/ subsidies
• Toilet access and safe management of sanitation in LICs is proportionate to those of citywide
• Equitable use of public finance across populations and communities
• HH & users’ costs to access sanitation services are equitable across the city
• Gender intentional representation in decision- making
• Sanitation workers’ rights, protections, and safety nets
Services safeguard customers, workers, and communities from safety and health risks—reaching everyone with safe sanitation
• Residents and city users have access to adequate toilet facilities in residential, community & public spaces, schools & healthcare facilities.
• Toilet facilities and waste services are managed to protect public health and environmental outcomes
• Waste disposal and treatment facilities are sufficient and operational
Services are reliably and continually delivered based on effective management of human, financial and natural resources
• Cost recovery of service delivery system operating expenses
• Financing resources for CAPEX expansion and renewal
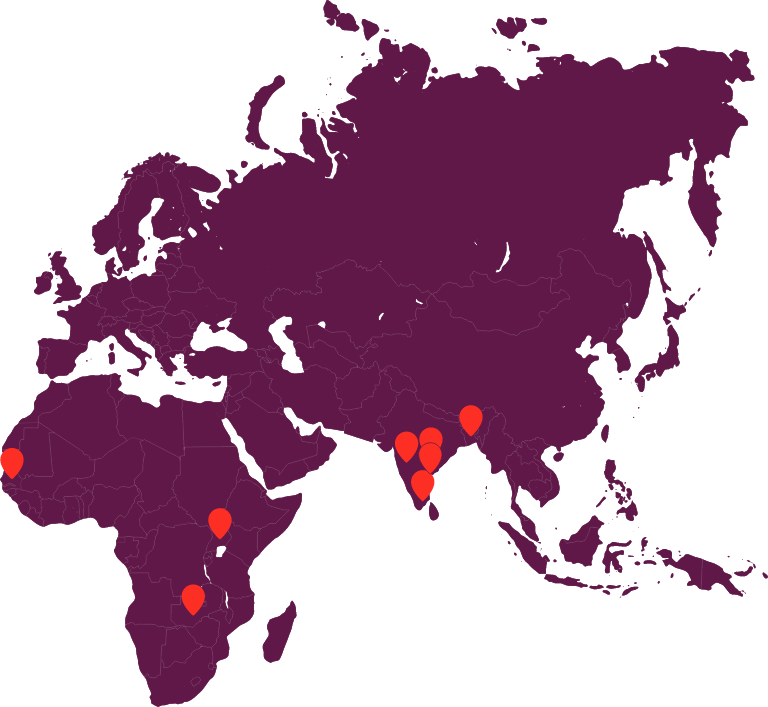
The eight CWIS cities represent a diverse range of demographic, geographic, and sanitation system characteristics. Each city is taking its unique path to overcome challenges and achieve common CWIS goals. Click on the city to learn more about their CWIS initiatives.
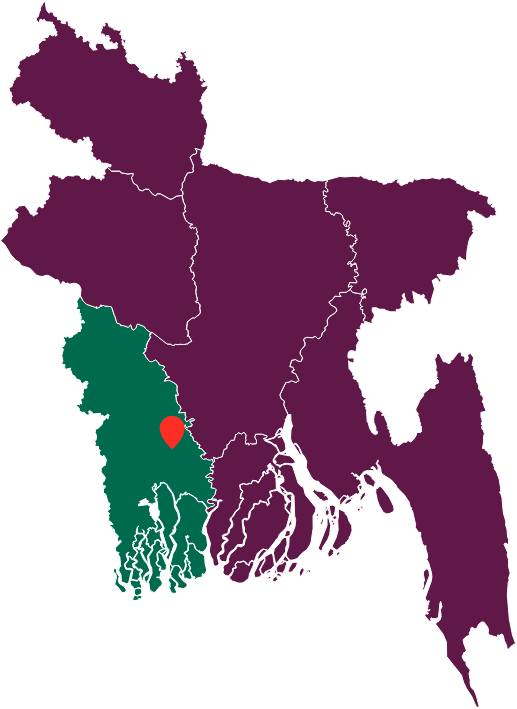
Khulna, Bangladesh
Population: 1.5 million
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 100% (as of 2020)
Partner Organization: SNV Netherlands Development Organisation (NGO)
CWIS Highlights:
- Khulna City Corporation (KCC) introduced an Integrated Municipal Information System (IMIS) to link data collected from Fecal Sludge Management (FSM) services with that from other municipal services including holding tax, trade licenses for business, and other tariff processes.
- Khulna constructed its first ever Fecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) with a capacity of 180 KLD, which can treat almost 40% of the fecal sludge generated in the city.
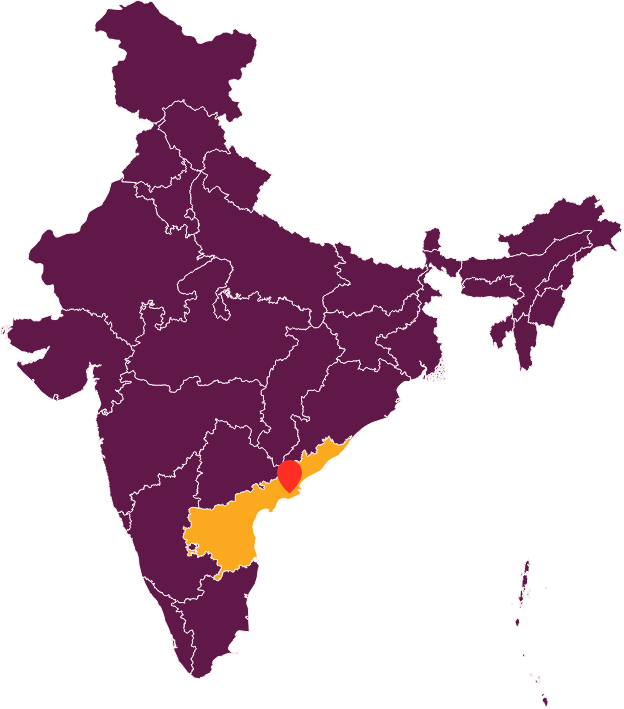
Narsapur, India
Population: 58,000
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 100%
Partner Organization: Administrative Staff College of India (Technical Support Unit)
CWIS Highlights:
- The Narsapur Municipal Corporation (NMC) carried out a GIS-based sanitation survey of all the properties in the town followed by a vulnerability assessment and a gender audit. NMC has developed a gender-integrated city sanitation plan and implemented measures covering gender budget, gender forums, and livelihood for workers in sanitation.
- Narsapur set up its first FSTP based on pyrolysis technology. Learning from the Narsapur experience, the Andhra Pradesh State Government is scaling up FSTPs to all 76 municipalities in the state through PPP (Hybrid Annuity Model).
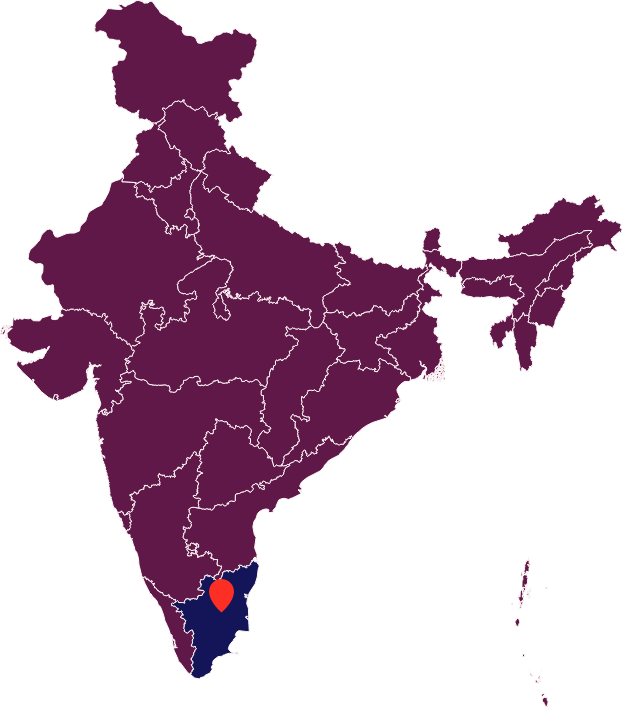
Trichy, India
Population: 900,000
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 55%
Partner Organization: Indian Institute of Human Settlement (Technical Support Unit)
CWIS Highlights:
- Trichy upgraded three of its four sewage pumping stations to decanting stations where desludging operators can dispose of the collected fecal sludge for co-treatment at the Sewage Treatment Plant. This also reduces the distance that the vacuum truck drivers have to travel.
- Trichy City Corporation (TCC) has empaneled all the private desludging operators in the city and uses a GPS based system to monitor the operation and disposal of FS. All operators are required to obtain a license from TCC with annual renewal, and are fined with a show-cause notice if they are found with illegal practice (illegal dumping or not wearing adequate protective gear).
Wai, India
Population: 43,000
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 100%
Partner Organization: Center for Water and Sanitation - CEPT University (Technical Support Unit)
CWIS Highlights:
- Wai is the first city in India to implement scheduled desludging. It is funded through the sanitation tax levied on all households, institutions, and commercial establishments, with the gap filled by Wai Municipal Council’s (WMC) own revenue from property tax surplus.
- To implement scheduled desludging, WMC engages a private desludging operator through a performance-based contract, and pays the service provider through an Escrow account with the local bank.
Warangal, India
Population: 800,000
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 100%
Partner Organization: Administrative Staff College of India (Technical Support Unit)
CWIS Highlights:
- The Greater Warangal Municipal Corporation (GWMC) has implemented innovative models of public toilets – exclusive toilets for women and toilets in fuel stations – via PPP, with service level agreements and ICT-based monitoring. Lessons are being scaled up across the State of Telangana.
- Warangal is the first city in the country to have passed Fecal Sludge and Septage Management (FSSM) regulations and to have operationalized two FSTPs. Informed by the Warangal experience, the State has scaled up FSTP development in 142 municipalities through PPP and public funding.
Dakar, Senegal
Population: 3.8 million
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 80%
Partner Organization: Office National de l'Assainissement du Sénégal (National Utility)
CWIS Highlights:
- ONAS has delegated all Fecal Sludge Treatment Plants (FSTPs) in Dakar to a group of private players through an affermage PPP model, wherein the private operators collect user fees and pay the public entity a fee for leasing the facilities.
- ONAS designed and built 100 innovative toilets for the flooded and flood-prone areas of Dakar, where the majority of the vulnerable population live. Beneficiary households were provided a sanitation loan to pay for the toilet, at 3% interest rate payable in 36 months.
Kampala, Uganda
Population: 1.5 million
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 92%
Partner Organization: Kampala Capital City Authority (City Government)
CWIS Highlights:
- Kampala developed a Sewage and Faecal Sludge Management Ordinance (2019), which now serves as the legal instrument for implementing FSM standards in the city.
- KCCA is piloting a new subsidy application to guide provision of subsidies for pit emptying services for vulnerable households in low income areas prone to diarrheal disease outbreaks. The subsidy targets women headed HHs among other factors.
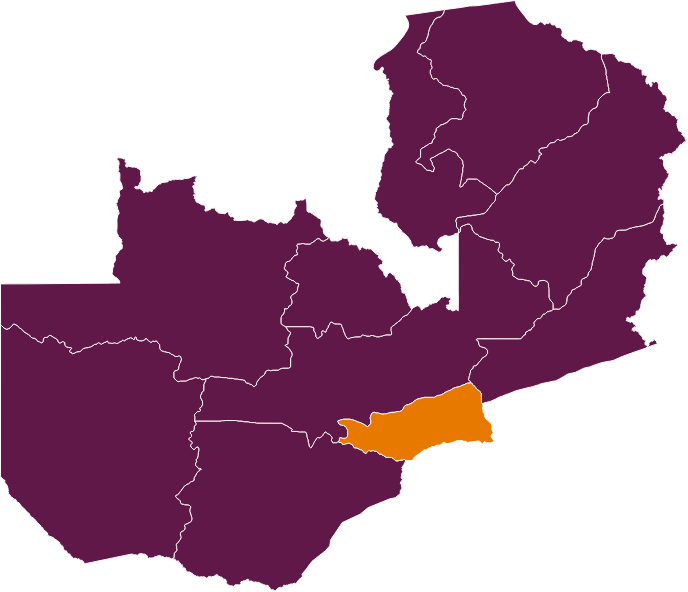
Lusaka, Zambia
Population: 2.5 million
Population Dependent on Onsite Sanitation: 84%
Partner Organization: Lusaka Water and Sanitation Company (Regional Utility)
CWIS Highlights:
- LWSC developed an FSM model for providing quality and safe emptying services to households not connected to the centralized sewer system. Six operators are currently serving households in low income settlements at an affordable cost.
- LWSC, Lusaka City Council (LCC) and Ministry of Health (MoH) jointly developed and operationalized an integrated M&E system, the Lusaka Sanitation System, to produce results on an agreed set of citywide indicators and share data.
The Monitoring, Learning, and Evidence (CWIS-MLE) program seeks to share progress in these eight cities, and to capture and communicate good practices, insights, and tools from the cities to facilitate a “learning and sharing while doing” approach among cities and for the sector.
This website is designed to be a platform both for showcasing early results from the program and for acting as a resource center for cities interested in learning about different intervention pathways attempted by these cities.
CWIS DASHBOARD
The CWIS dashboard is designed to help the CWIS city grantees monitor and track their progress from their baselines and quickly see how their peers are performing on similar metrics.

CWIS LEARNING
A collection of factsheets and learning briefs on and from the eight CWIS cities, aimed at providing insights into a range of questions on CWIS policy and implementation. Click here to view our library of CWIS documents.
Key Portfolio Summaries

CWIS City Snapshots
City Snapshots are compact summaries of CWIS initiatives that are being implemented in eight cities. These snapshots outline the pathway taken by each city to achieve its CWIS goals and tracks the progress being made, including key shifts in institutional and service delivery models to support safe, equitable and sustainable delivery of services.

CWIS factsheets
CWIS Factsheets are short cross-city summaries on topics that shed light on the CWIS outcomes of Equity, Safety, and Sustainability and system functions of Responsibility, Accountability, and Resource Planning and Management.
Download the CWIS Factsheet on

CWIS cross-city learning briefs
CWIS Learning Briefs are empirical observation and applied analysis of diverse approaches taken in the eight CWIS cities on common topics in delivering safe sanitation. These briefs are meant to facilitate peer learning, and delve into questions of practice, so that practitioners and implementing organizations can learn from one another.

City Data Plans
City Data Plans are city specific strategy recommendations for each of the eight CWIS cities to bridge data gaps and sustainably generate and update data for the CWIS indicators. The recommendations are being developed in consultation with city sanitation service authorities and technical support partners, based on data gaps identified for each city as presented on the CWIS Dashboard.
Reports coming soon!

CWIS data collection instruments
CWIS Data Collection Instruments are a set of survey instruments and Key Informant Interview (KII) guides for quantitative and qualitative data collection for CWIS. The instruments are designed to be compatible with existing global standards while allowing ample room for national level authorities to drive their own reform priorities, and for city service authorities to collect the data required for local decision-making and intervention design. These instruments will serve as a reference tool for anyone interested in mapping their city sanitation ecosystem from a CWIS lens.
Data Collection Instruments coming soon!
CWIS initiatives are being implemented in eight cities by seven partners, including ASCI, CEPT, IIHS, KCCA, LWSC, ONAS, and SNV. Athena Infonomics is the MLE partner supporting these seven lead partners on monitoring and learning. The CWIS programs in these eight cities and the MLE initiative are funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Interested in knowing more about the CWIS MLE program, the CWIS measurement framework, or potential collaboration? Email us at kun.z@athenainfonomics.com








